I was talking to Franz Schelling earlier today and a couple of examples came up in conversation that I think are of interest here as well (Thanks to Franz)

Abstract
PRIMARY OBJECTIVE:
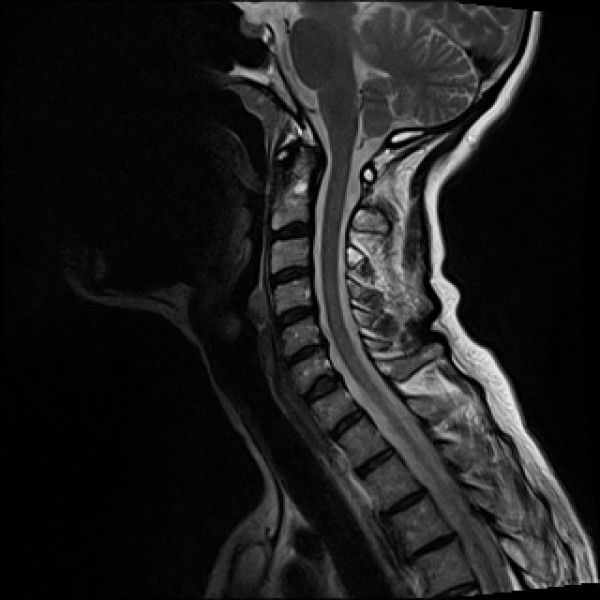
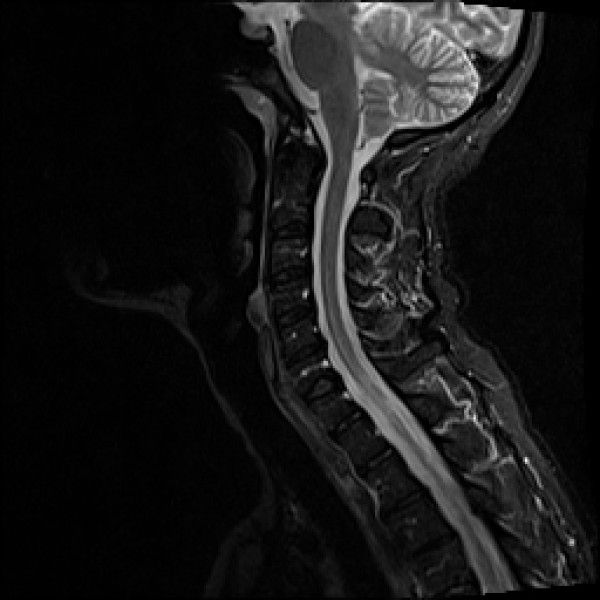
Chiari malformation is defined as herniation of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum, also known as cerebellar tonsillar ectopia (CTE). CTE may become symptomatic following whiplash trauma. The purpose of the present study was to assess the frequency of CTE in traumatic vs non-traumatic populations.
STUDY DESIGN:
Case-control.
METHODS AND PROCEDURES:
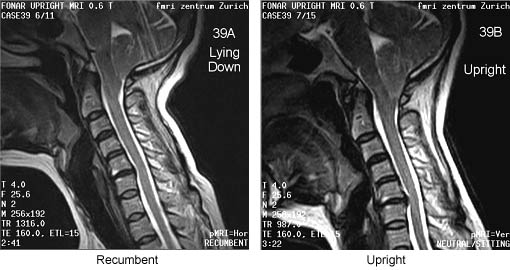
Cervical MRI scans for 1200 neck pain patients were reviewed; 600 trauma (cases) and 600 non-trauma (controls). Half of the groups were scanned in a recumbent position and half were scanned in an upright position. Two radiologists interpreted the scans for the level of the cerebellar tonsils.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND RESULTS:
A total of 1195 of 1200 scans were read. CTE was found in 5.7% and 5.3% in the recumbent and upright non-trauma groups vs 9.8% and 23.3% in the recumbent and upright trauma groups (p = 0.0001).
CONCLUSIONS:
The results described in the present investigation are first to demonstrate a neuroradiographic difference between neck pain patients with and without a recent history of whiplash trauma. The results of prior research on psychosocial causes of chronic pain following whiplash are likely confounded because of a failure to account for a possible neuropathologic basis for the symptoms.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20545453
and
The spinal cords were examined in eighteen cases of multiple sclerosis, with special attention to the cervical enlargement. It was found that (1) lesions in the cervical cord are about twice as common as at lower levels, (2) in this region there is a striking preponderance of fan-shaped lesions in the lateral columns. It is argued that both these findings are explicable on the theory that mechanical stresses play a part in determining the site of lesions; that such stresses are commonly transmitted to the cord via the denticulate ligaments during flexion of the spine; and that many of the lesions are attributable to vascular leakages due to tension in the denticulate ligaments. It is concluded that in patients with multiple sclerosis neck flexion is dangerous–especially in cases where Lhermitte's sign has occurred.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1 ... x/abstract

Nigel